The Snub Disphenoid
The snub disphenoid is the 84th Johnson solid (J84). Its surface consists of 12 equilateral triangles, 18 edges, and 8 vertices.
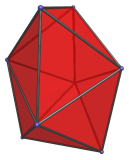
It is also known as the Siamese dodecahedron
because it has 12 faces
and can be formed by conjoining two regular octahedra
each with a pair of triangles removed and the remaining 6 faces slightly
deformed, like Siamese twins (conjoined twins).
Another way to construct it is to split a tetrahedron, regarded as a digonal antiprism ("disphenoid"), into two pairs of triangles, suitably deformed, and joining them with a band of 8 triangles ("snubbing"). Hence the name snub disphenoid. A similar process applied to the octahedron, regarded as a triangular antiprism, produces the regular icosahedron; and when applied to the square antiprism, produces the snub square antiprism (J85).
It is one of the special Johnson solids at the end of Norman Johnson's list that are not directly derived from the uniform polyhedra by cut-and-paste operations.
Projections
Here are some views of the snub disphenoid from various angles:
| Projection | Envelope | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
Square | Top view. |
 |
Irregular pentagon | Side view. |
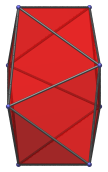 |
Irregular octagon | Oblique side view at 45° angle. |
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the snub disphenoid, centered on the origin with edge length 2, are:
- (0, √A, ±1)
- (±√C, √B, 0)
- (0, −√B, ±√C)
- (±1, −√A, 0)
where A, B, and C are the roots of the following polynomials within the indicated ranges:
| 2A3 − A2 − 8A − 4 = 0, | 2 ≤ A ≤ 3 |
| 2B3 + 11B2 + 4B − 1 = 0, | 0 ≤ B ≤ 1 |
| C3 − 17C2 + 64C − 64 = 0, | 1 ≤ C ≤ 2 |
Their numerical values are approximately:
- A = 2.458190775872486
- B = 0.169022229424176
- C = 1.661955541151648
Their square roots are approximately:
- √A = 1.567861848465127
- √B = 0.411123131706519
- √C = 1.289168546448310




