The Decagonal Antiprism
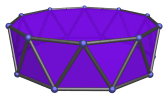
The decagonal antiprism is a 3D uniform polyhedron bounded by 22 polygons (2 decagons and 20 triangles), 40 edges, and 20 vertices.
The height of a decagonal antiprism with an edge length of 2 is:
2√(√(11φ+7)−2φ−1)
or approximately 1.724794, where φ=(1+√5)/2 is the Golden Ratio.
A decagonal antiprism can be attached to a pentagonal cupola (J5) to make a gyroelongated pentagonal cupola (J24), or attached to a pentagonal rotunda (J6) to make a gyroelongated pentagonal rotunda (J25).
Inserting a decagonal antiprism between two pentagonal cupolae produces the gyroelongated pentagonal bicupola (J46). Doing so between a pentagonal cupola and a pentagonal rotunda produces the gyroelongated pentagonal cupolarotunda (J47); and doing so between two pentagonal rotundae produces the gyroelongated pentagonal birotunda (J48).
Projections
Here are some views of the decagonal antiprism from various angles:
| Projection | Envelope | Description |
|---|---|---|
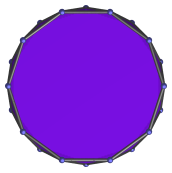 |
Regular dodecagon | Parallel projection centered on decagonal face. |
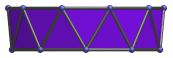 |
Trapezium | Parallel projection parallel to square faces and a pair of triangles. |
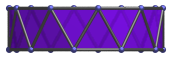 |
Rectangle | 9° side view. |
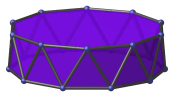 |
Hendecagon | Parallel projection centered on vertex. |
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the decagonal antiprism, centered on the origin and having edge length 2, are:
- (±2φ, 0, H)
- (±1, ±√(3+4φ), H)
- (±φ2, ±√(2+φ), H)
- (0, ±2φ, −H)
- (±√(3+4φ), ±1, −H)
- (±√(2+φ), ±φ2, −H)
where φ = (1+√5)/2 is the Golden Ratio, and H = √(√(11φ+7)−2φ−1), or approximately 0.862397, is half the height of the antiprism.




