The Cuboctahedron
The cuboctahedron is a uniform polyhedron bounded by 14 polygons (6 squares and 8 triangles), 24 edges, and 12 vertices. It is edge-uniform, and its two kinds of faces alternate around each vertex, so it is also a quasi-regular polyhedron. It may be constructed by truncating a cube or an octahedron at the midpoints of its edges (this process is known as rectification).
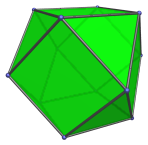
The cuboctahedron can be bisected by a plane parallel to two opposite triangular faces to produce the triangular cupola (J3), a Johnson solid.
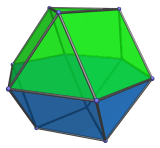
The dual of the cuboctahedron is the rhombic dodecahedron, a Catalan solid.
Projections
In order to be able to identify the cuboctahedron in various projections of 4D objects, it is useful to know how it appears from various viewpoints. The following are some of the commonly-encountered views:
| Projection | Envelope | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
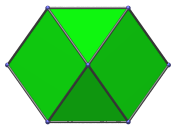
Square | Parallel projection centered on a square face. |
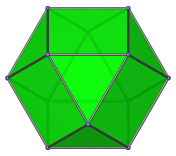 |
Regular hexagon | Parallel projection centered on a triangular face. |
 |
Hexagon | Vertex-first projection. |
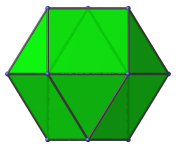 |
Hexagon | Edge-first projection. |
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the cuboctahedron, centered on the origin and having edge length 2, are all permutations of coordinates and changes of sign of:
- (0, √2, √2)
Occurrences
The cuboctahedron occurs as cells in a variety of 4D uniform polytopes:
- The cantellated 5-cell;
- The runcitruncated 5-cell;
- The rectified tesseract;
- The runcitruncated tesseract;
- The rectified 24-cell;
- The cantellated 24-cell;
- The runcitruncated 120-cell;
- The cantellated 600-cell.
Some CRF polychora also contain cuboctahedral cells, including (but not limited to):




